Inheritance is an important pillar of OOP(Object Oriented Programming). It is the mechanism in java by which one class is allow to inherit the features(fields and methods) of another class.
Inheritance represents the IS-A relationship which is also known as a parent-child relationship.
Important terminology:
- Super Class: The class whose features are inherited is known as super class(or a base class or a parent class).
- Sub Class: The class that inherits the other class is known as sub class(or a derived class, extended class, or child class). The subclass can add its own fields and methods in addition to the superclass fields and methods.
- Reusability: Inheritance supports the concept of “reusability”, i.e. when we want to create a new class and there is already a class that includes some of the code that we want, we can derive our new class from the existing class. By doing this, we are reusing the fields and methods of the existing class.
There are 4 types of inheritance
- Single inheritance
- Multilevel inheritance
- Hierarchical inheritance
- Multiple inheritance
Example of Inheritance,
class Bicycle { // the Bicycle class has two fields public int gear; public int speed; // the Bicycle class has one constructor public Bicycle(int gear, int speed) { this.gear = gear; this.speed = speed; } // the Bicycle class has three methods public void applyBrake(int decrement) { speed -= decrement; } public void speedUp(int increment) { speed += increment; } // toString() method to print info of Bicycle public String to String() { return("No of gears are "+gear +"\n"+ "speed of bicycle is "+speed); } } // derived class class MountainBike extends Bicycle { // the MountainBike subclass adds one more field public int seatHeight; // the MountainBike subclass has one constructor public MountainBike(int gear,int speed, int startHeight) { // invoking base-class(Bicycle) constructor super(gear, speed); s eatHeight = startHeight; } // the MountainBike subclass adds one more method public void setHeight(int newValue) { seatHeight = newValue; } // overriding toString() method // of Bicycle to print more info @Overridepublic String toString() { return (super.toString()+ "\nseat height is "+seatHeight); } } // driver class public class Test { public static void main(String args[]) { MountainBike mb = new MountainBike(3, 100, 25); System.out.println(mb.toString()); } } |
Output:
No of gears are 3 speed of bicycle is 100 seat height is 25
In above program, when an object of MountainBike class is created, a copy of the all methods and fields of the super class acquire memory in this object. That is why, by using the object of the sub class we can also access the members of a parent class.
Please note that during inheritance only object of child class is created, not the parent class.
SINGLE INHERITANCE :
Single Inheritance : In single inheritance, sub classes inherit the features of one superclass. In image below, the class A serves as a base class for the derived class B.

class child class
{…. methods
}
class derived class name extends child class
{
methods … along with this additional feature
Example program of single inheritance ,
class Shape {
public void display()
{
System.out.println("Inside display");
}
}
class Rectangle extends Shape
{
public void area()
{
System.out.println("Inside area");
}
}
public class Tester {
public static void main(String[] arguments)
{
Rectangle rect = new Rectangle();
rect.display();
rect.area();
}
}
Output
Inside display Inside area
Here Rectangle class inherits Shape class and can execute two methods, display() and area() as shown.
MULTILEVEL INHERITANCE :
class Shape {
public void display() {
System.out.println("Inside display");
}
}
class Rectangle extends Shape {
public void area() {
System.out.println("Inside area");
}
}
public class Tester {
public static void main(String[] arguments) {
Rectangle rect = new Rectangle();
rect.display();
rect.area();
}
}
Output
Inside display Inside area
Here Rectangle class inherits Shape class and can execute two methods, display() and area() as shown.
MULTILEVEL INHERITANCE :
When a class extends a class, which extends anther class then this is called multilevel inheritance. For example class C extends class B and class B extends class A then this type of inheritance is known as multilevel inheritance.
Lets see this in a diagram:
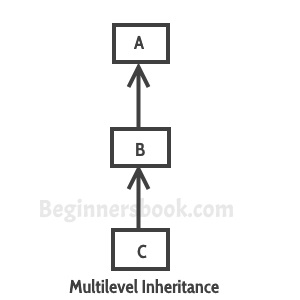
class Car
{
public Car()
{
System.out.println("Class Car");
}
public void vehicleType()
{
System.out.println("Vehicle Type: Car");
}
}
class Maruti extends Car
{
public Maruti()
{
System.out.println("Class Maruti");
}
public void brand()
{
System.out.println("Brand: Maruti");
}
public void speed()
{
System.out.println("Max: 90Kmph");
}
}
public class Maruti800 extends Maruti
{
public Maruti800()
{
System.out.println("Maruti Model: 800");
}
public void speed()
{
System.out.println("Max: 80Kmph");
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
Maruti800 obj=new Maruti800();
obj.vehicleType();
obj.brand();
obj.speed();
}
}
Output:
Class Car Class Maruti Maruti Model: 800 Vehicle Type: Car Brand: Maruti Max: 80Kmph HIERARCHIAL INHERITANCE : A situation in which a parent class is inherited by many subclasses is called hierarchical inheritance. This is shown in the following diagram, where A is a parent class and B, C, and D are child classes. In this inheritance model, two or more classes are derived from the parent class: 
package P1;class Employee{float salary = 40000;}
class PermanentEmp extends Employee
{
double hike = 0.5;
}
class TemporaryEmp extends Employee
{
double hike = 0.35;
}
public class HerInheritanceDemo
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
PermanentEmp p = new PermanentEmp();
TemporaryEmp t = new TemporaryEmp();
// All objects of inherited classes can access the variable of class Employee
System.out.println("Permanent Employee salary is :" +p.salary); System.out.println("Hike for Permanent Employee is:" +p.hike); System.out.println("Temporary Employee salary is :" +t.salary); System.out.println("Hike for Temporary Employee is :" +t.hike);
}
}
Output: 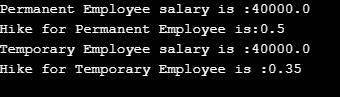 As in the above code, PermanentEmp class and TemporaryEmp classes are the subclass and Employee is the superclass and objects of these subclasses are accessing the variable of the superclass, which shows the hierarchal inheritance concept or feature in Java.
As in the above code, PermanentEmp class and TemporaryEmp classes are the subclass and Employee is the superclass and objects of these subclasses are accessing the variable of the superclass, which shows the hierarchal inheritance concept or feature in Java.
MULTIPLE INHERITANCE :
When one class extends more than one classes then this is called multiple inheritance. For example: Class C extends class A and B then this type of inheritance is known as multiple inheritance. Java doesn’t allow multiple inheritance.
Why multiple inheritance is not supported in java?
To reduce the complexity and simplify the language, multiple inheritance is not supported in java.
Consider a scenario where A, B, and C are three classes. The C class inherits A and B classes. If A and B classes have the same method and you call it from child class object, there will be ambiguity to call the method of A or B class.
Since compile-time errors are better than runtime errors, Java renders compile-time error if you inherit 2 classes. So whether you have same method or different, there will be compile time error.
- class A{
- void msg(){System.out.println(“Hello”);}
- }
- class B{
- void msg(){System.out.println(“Welcome”);}
- }
- class C extends A,B{//suppose if it were
- public static void main(String args[]){
- C obj=new C();
- obj.msg();//Now which msg() method would be invoked?
- }
- }
after compiled Error occured.